A Comparative Look at the 8 Leading Political Systems
History, Evolution and Modern Politics
Political systems are a fundamental part of human societies, they overlook all the matters and ensure growth in a society. Government systems are essential to provide people with their rights, security and potential to thrive. To maintain law and order and the serenity of a state, different territories use different techniques but all have a common purpose to preserve their traditions and healthy lifestyle.
What are the 8 leading political systems:-
Democracy: Power to the People:-
Origin:-
Democracy is derived from the Greek words “demos” and “kratos”.
- Demos means “people”
- Kratos means “rule”
Hence, the rule of the people. Democracy was first established in Athens, Greece 🇬🇷 by a statesman named Cleisthenes also regarded as “father of Athenian democracy” in 508 BCE. Although Athenian democracy differs in various ways from today’s democracy, it paved the footsteps for modern democracy.
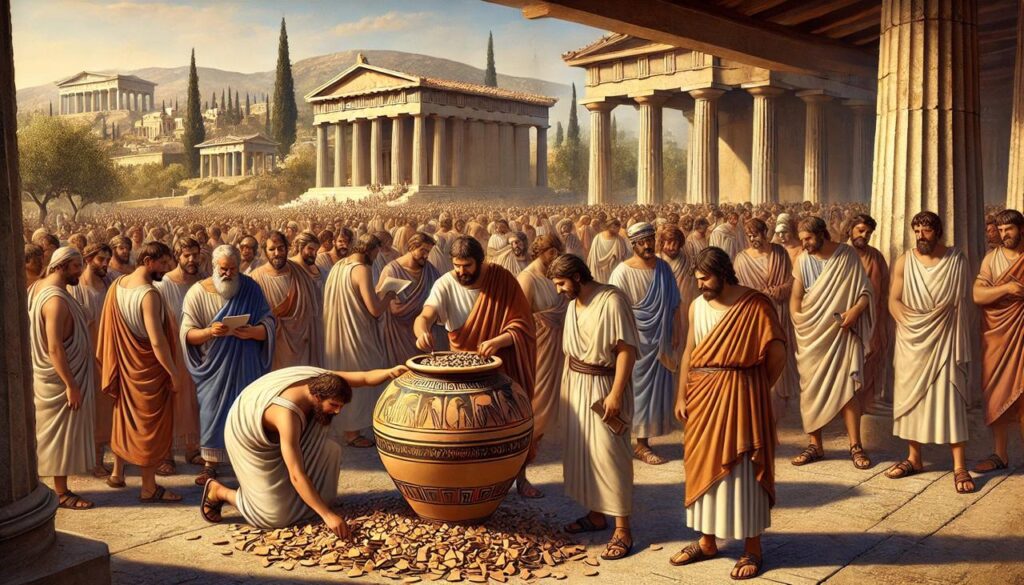

Why was there a need for Democracy?
Before democracy in Athens, the possession of the state was in the hands of a few aristocracies. They started to exploit their powers and economic disparities grew between the rich and the poor. The elites often made conclusions which were favourable to them ignoring the needs of the poor. Due to the tremendous difference between the rich and poor’s quality of life, and to stop the abuses of the nobility, people commenced mandating their liberties.
Preservation of Rights:-
Modern-day democracy gives complete freedom and domination to the people, but to keep harmony in society, the Constitution and justice system were constructed. The Constitution gives rights to the populace and simultaneously protects the rights of the minority. For example: if the majority decides to harm a minority, the law won’t allow it and justice will prevail through a system of courts. Democratic governments provide people with the liberty to prefer how they desire to live their lives instead of a monarch’s decree supervising them.
Types of democracy:-
Although there exist various forms of democracy the foundational types are:
Direct democracy:-
Direct democracy:-
In direct democracy, people directly take part and vote on all the bills and legislation. For example: in Switzerland 🇨🇭 and Liechtenstein 🇱🇮.
Representative democracy:-
In representative democracy, people elect a representative through voting to make decisions on their behalf. For example: in Canada 🇨🇦, Australia 🇦🇺 and Germany 🇩🇪.

Monarchy: Power to One:-
Origin:-
The earliest documented history of monarchy can be found in ancient Egypt 🇪🇬 under the rule of Menes – a pharaoh also known as Narmer in 3100 BCE (date is debatable) and a Sumerian King of Kish in 2600 BCE (date is debatable). Sumer, an ancient civilization, was between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers in modern-day south Iraq 🇮🇶. Though monarchy existed before these civilizations, due to the scarcity of historical records we can’t make a bold statement.
Why was Monarchy established?
As the human population increased, so did the need for resources and industries. To preserve the tranquillity of the tribe, the noble and the powerful took responsibility and came into a position of authority. They managed all the resources and provided tribal people with justice and security. Conquests of other tribes led to expansion and soon tribes became kingdoms. Thus, to govern such a situation a hierarchal system, monarchy, was concocted and the one with the supreme position was referred to as a Monarch.
Modern-day monarchies:-
There are various types of monarchies but two are primary:
Absolute Monarchy:-
The control of the state is in the hands of the sovereign and he has the supreme authority. Their words are the last and can’t be questioned. Examples: Kingdom of Saudi Arabia 🇸🇦 Oman 🇴🇲, and Brunei 🇧🇳.
Constitutional Monarchy:-
The powers of the king and the queen are limited by the constitution and there is another government system which holds the power. The king and queen are accustomed to obeying the system. Modern-day examples are the UK 🇬🇧, Sweden 🇸🇪, Denmark 🇩🇰 and Japan 🇯🇵.

Theocracy: Rule of God:-
Origin:-
Theocracy is derived from the Greek words “theos” and “kratos”.
- Theos means “god”
- Kratos means “rule”
Hence, the rule of the god. The earliest documented history of theocracy can be obtained from ancient Egypt 🇪🇬 in 3100 BCE (date is debatable). Though it was a monarchy simultaneously it acted like a theocracy. Theocracy is a type of government in which the rule of god prevails and religious leaders take command. Pharaohs believed that they were semi-deities and people used to worship them. This belief granted them authority as divine leaders.
Idea of Theocracy:-
Since the dawn of mankind, religion has been a crucial part of our daily life. In different cultures and tribes, diverse religious beliefs were settled. Although the main idea was the same to bring society together and maintain the serenity of the world. Few people were more religious than others and a few claimed divinity or were deeply connected with spirituality. People respected them and trusted them with their vitalities and tough decisions. They took the responsibility of the public and slowly gained power. One possibility led to another possibility and a political system appeared where a religious ruler took power and formed laws based on the religion of the majority.
Examples of theocracy:-
Old theocracy:-
The oldest theocratic governments were of Egypt (3100 BCE) and Mesopotamia (2900 BCE) where kings were considered representatives of god or semi-deities. Later, in ancient Israel, some notable personalities were the Prophet Moses (1300-1200 BCE), Prophet David (1010-970 BCE) and Prophet Solomon (970-931 BCE). Even in the Middle Ages, there were various empires example: the Byzantine Empire, the Holy Roman Empire and Islamic Caliphates.
Modern-day theocracy:-
Modern-day examples of theocratic nations are the Vatican City 🇻🇦(established in 1929) where the pope is in charge of the government and Iran 🇮🇷 (established in 1979) under the supreme leader with authority over political and religious matters (currently Ayatollah Ali Khamenei).

Oligarchy: Rule of Few:-
Oligarchy is derived from the Greek words “oligos”
and “arkhein”.
- Oligos means “few”
- Arkhein means “to rule”
Hence, the rule of few people. Oligarchy existed in various Greek cities, for example: Athens and Sparta, before democracy. Aristotle analyzed and elucidated various political systems. He described its characteristics and compared it to other political systems.
Oligarchy vs Monarchy:-
Oligarchy is a governance system in which the authority lies in the hands of a few nobilities. They decide the future of the state and regulate international policies. They furthermore operate all the country’s resources and concerns.
The question arises: what’s the difference between oligarchy and monarchy?
Well, in a monarchy the power remains in specific lineages and seats of authority are inherited by their juveniles. Whereas, in an oligarchy, one might rise to power through military might and economic resources. Thus, in an oligarchy families might change over the years and new potent individuals would ascend. According to Aristotle: “Oligarchy was the perverted form of aristocracy”.
Examples:-
After Sparta Athens and other Greek cities, there were various other examples which existed in medieval times. In modern-day Oligarchy the most prominent example is Russia 🇷🇺. Russia after the soviet union experienced an oligarchy in the 1990s.

Totalitarianism: Rise of Nationalism:-
Origin:-
Totalitarianism was adopted by several countries in the 20th century. The concept was first introduced by Benito Mussolini – leader of Italy, in the 1920s. Later, it was adopted by several countries in which prominent countries were Germany 🇩🇪 under Adolf Hitler ( 1933-1945) and the Soviet Union under Joseph Stalin (1922-1953).
20th Century Europe:-
In the first half of the 20th century, European countries underwent economic turmoil. Due to the “great economic depression” in the 1930s widespread poverty and unemployment rates were the dirges of nations. Inflation was at an all-time high and masses were drawn into the abyss of dread.
Popular leaders:-
To ensure their prosperity and safety, nations darted for a heroic personality. Leaders like Adolf Hitler and Joseph Stalin rose to power due to their charisma and vowed to carry the homeland back to its grounds and to deliver stability and serenity. What happened next? They manipulated the masses through their oratory skills and fostered extreme nationalism. They made regulations which aligned best with their welfare in the name of nationalism while disregarding the Constitution. They also suppressed other parties forming a single-party rule and complete hegemony over every sector. Thus, this specific governance system is regarded as “totalitarianism”.
Modern-day totalitarianism:-
A modern-day example of totalitarianism is Eritrea 🇪🇷, a country in Africa under President Isaias Afwerki. He was the first president of the country after its independence from its neighbour Ethiopia 🇪🇹 in 1993. Another more eminent example is North Korea 🇰🇵, under the Kim dynasty since 1948. Korea attained their independence from Japan in 1945, after the USSR and USA 🇺🇸 were incapable of finding a path to unify the country, they constituted two separate states in 1948.

Communism: People are Equal:-
Origin:-
The crafting of communism is credited towards two 19th-century men Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. They both published a pamphlet in 1848 called “The Communist Manifesto”. Communism is a governance system in which the property is owned by communities rather than individuals and each individual contributes to his extent and acquires according to his conditions and necessities. Communism was first executed on a large scale in 1917 in Russia 🇷🇺 under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin and laid footsteps for the future states to follow.
Communism vs Capitalism:-
To deal with the 19th-century chaos, it was assumed capitalism was the reason for the collapse. Due to economic inequality, the world experienced different classes and often the rich exploited the peasants by giving them minimal salaries for strenuous labour. To ensure future stability the concept of communism was publicized to initiate a classless society. To apply it they abolished all private ownership and believed it to be the way to equality and the end of oppression. Marx and Engels state communism is the response to capitalism and the outcome of historical evolution. In this way, a modest society will be originated and the public will live in harmony and satisfaction. In the Manifesto a remarkably renowned line is
“Workers of the world, unite! You have nothing to lose but your chains”.
Modern-day communist nations:-
In modern society, there are still several countries that follow a communist way of governance. In which the most notable is China 🇨🇳 currently under Xi Jinping, other examples are Cuba 🇨🇺 and Laos 🇱🇦.

Feudalism: Popular Middle Ages System:-
Origin:-
If we go back to the roots, we will discover the earliest form of feudalism originated from the Zhou dynasty in China 🇨🇳. Later, the Romans introduced a manorial system which had remnants of the feudal system in Europe. Tardily it flared all over Europe in the Middle Ages (9th-15th century BCE) and evolved completely into feudalism.
How does feudalism work:-
When empires prospered into immense powers and became oversized, it became difficult for the King to govern them. To ensure stability and serenity, a new governance system evolved “feudalism”. Emperors gave the authority of their lands (fiefs) to the Lords in return for military service and loyalty. Lords often created smaller portions of the land and allotted it to the vassals (knights) in exchange for military service and devotion to the Lords and King. At the bottom of the hierarchy were the peasants (serfs) who were provided with food, shelter and protection and owned no land. In return, they worked for the nobility, mainly on farms to ensure food production.
Feudalism in Europe:-
Feudalism remained a prevalent governance system in Europe for centuries. The first feudal empire in Europe is known as “The Carolingian Empire” was founded by “Charlemagne” in the year 800. Later, various kingdoms in Europe adopted it, prominent examples are the Holy Roman Empire, the Kingdom of France 🇫🇷 (843-1792), the Kingdom of England (10th century- 1707), the Kingdom of Hungary 🇭🇺 (1000-1918) and the Kingdom of Poland 🇵🇱 (1025-1795).
End of feudalism:-
There were varied factors that contributed to the gradual downfall of feudal empires. In the late Middle Ages, the peasants (serfs) revolted against the Lords and urged more rights and freedoms. Later, the economic changes in the world led to land not being the primary source of wealth and the prevalent philosophical ideas of equality and autonomy played a vital role in modern-day government systems, various other factors furthermore marked the end of feudalism and in modern times there exists no feudal empire.

Anarchy: Rule of None:-
Origin:-
Anarchy is derived from the Greek word “anarchia” meaning “without a ruler”. Various individuals advocated anarchy in their manner but the most eminent is Pierre-Joseph Proudhon (1809-1865) – the father of anarchism. Anarchism is a design in which a society is not supervised by a governance system and the masses self-govern themselves and willingly assist each other. Pierre-Joseph Proudhon voiced:
“As man seeks justice in equality, so society seeks order in anarchy”.
Why anarchy?:-
Anarchism was established to end tyranny and totalitarian regimes as officials of states began to abuse their hegemony and torment the populace. They opposed hierarchal systems, were advocates of equivalency and autonomy and resisted capitalism as it created economic disparity and a few people (elites) had command over the state. Supporters of anarchism disapproved of private ownership, Pierre-Joseph Proudhon spoke out: “Property is theft”!
Flaws of anarchism:-
The question emerges:
How will a society run without a government? The reply is: It can’t.
Just like any other government system, anarchism has its imperfections. Due to the lack of government, there will be no composure and order in the society. Without a centralized system, the resources can’t be managed and new developments can’t emerge. There will be no justice and the whole of society will fall into a dark abyss and serenity would be an old poem.
Diversity:-
Though every human is equal, since the dawn of man there have been different burdens on different people and there have invariably been nobilities and peasants, courageous and cowards, selfish and selfless in human history. Therefore, rather than focusing on the differences and flaws of each other, we must accept diversity.
20th century examples:-
The first-ever anarchic state formed during the Russian Civil War, when a part of Ukraine 🇺🇦 (1918-1921) was under no surveillance. Another example of anarchy was in Spain 🇪🇸 (1936-1939) at the time of the Spanish Civil War.
Modern-day examples:-
In modern days there is anarchy on a very miniature scale, for example: Christiana in Copenhagen, Denmark 🇩🇰 (since 1971), Rojava in Syria 🇸🇾 (since 2012) and Zapatista autonomous municipalities in Mexico 🇲🇽 (1994-present).

“History and Politics deciphered: Clear Answers For Complex World.”
Suleman Junaid
Writer, Publisher: History and politics